
Use the mount command to mount a shared NFS directory from another machine, by typing a command line similar to the following at a terminal prompt: sudo mkdir /opt/example
NFS MANAGER MAC DOWNLOAD INSTALL
To enable NFS support on a client system, enter the following command at the terminal prompt: sudo apt install nfs-common no_root_squash, for example, adds a convenience to allow root-owned files to be modified by any client system’s root user in a multi-user environment where executables are allowed on a shared mount point, this could lead to security problems.

These settings each have their own trade-offs so it is important to use them with care, only as needed for the particular use case. There are a number of optional settings for NFS mounts for tuning performance, tightening security, or providing conveniences. Like with sync, exportfs will warn if it’s left unspecified. Read-only filesystems are more suitable to enable subtree_check on.
NFS MANAGER MAC DOWNLOAD VERIFICATION
This verification step has some performance implications for some use cases, such as home directories with frequent file renames. Subtree_check and no_subtree_check enables or disables a security verification that subdirectories a client attempts to mount for an exported filesystem are ones they’re permitted to do so. Even though sync is the default, it’s worth setting since exportfs will issue a warning if it’s left unspecified. async thus gives a performance benefit but risks data loss or corruption. The sync/ async options control whether changes are gauranteed to be committed to stable storage before replying to requests. Make the hostname declaration as specific as possible so unwanted systems cannot access the NFS mount. You can replace * with one of the hostname formats. Make sure any custom mount points you’re adding have been created (/srv and /home will already exist): sudo mkdir /scratchĪpply the new config via: sudo exportfs -a scratch *(rw,async,no_subtree_check,no_root_squash) For example: /srv *(ro,sync,subtree_check) You can configure the directories to be exported by adding them to the /etc/exports file. To start the NFS server, you can run the following command at a terminal prompt: sudo systemctl start rvice This may reduce the number of removable media drives throughout the network.Īt a terminal prompt enter the following command to install the NFS Server: sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server
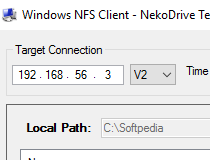
Storage devices such as floppy disks, CDROM drives, and USB Thumb drives can be used by other machines on the network. Home directories could be set up on the NFS server and made available throughout the network. There is no need for users to have separate home directories on every network machine. Local workstations use less disk space because commonly used data can be stored on a single machine and still remain accessible to others over the network. Some of the most notable benefits that NFS can provide are: By using NFS, users and programs can access files on remote systems almost as if they were local files. NFS allows a system to share directories and files with others over a network. Multi-node Configuration with Docker-Compose


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
